Sustainability in Computing Education
Sustainability in Computing Education
Click here for examples of sustainability analysis for Bachelor/Master theses
What is Sustainability?
Sustainable development can be defined as 'development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs'.
- Brundtland, Gro H. «Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future». United Nations Conference on Environment and Development. United Nations World Commission on Environment and Development, 1987.
What do the course descriptions say about Bachelor’s and Master’s theses?
The course description for, among others, the Master’s theses in Computer Engineering and Computer Science emphasizes reflection on the relevance of the thesis for sustainable development, where students should assess how the thesis relates to the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
|
The thesis should reflect on the sustainability relevance of the work based on the UN Sustainable Development Goals |
We can also see similar elements in the assignment description for Digital Transformation: Digital Transformation:
|
In the Master’s thesis, reflection should be made on the sustainability relevance of the thesis based on selected elements from UNESCO’s 8 key competencies for sustainability or the UN Sustainable Development Goals. |
Another criterion that examiners look for is a critical assessment of one’s own work, so it is advisable to write about sustainability in the thesis. Both the Master’s thesis in Computer Engineering and Computer Science emphasize that one must “(...) critically assess the work and contribution.” (Figure 1). The course description for the Master’s in Digital Transformation, states that students should “Exhibit a research-ethical and sound critical attitude towards the research work.” If you develop a technological solution without considering the sustainability consequences, you may overlook important aspects such as resource use, environmental impact, social responsibility, and economic sustainability. Therefore, it is important to reflect on how the solution affects society and the environment, which will strengthen the quality and relevance of the thesis.
|
Academic content |
Figure 1: The requirements for academic content in the Master’s thesis in Computer Science and Computer Engineering specify that one must “critically assess the work and contribution”
From previous Master’s theses, some common features can be observed in projects with clear critical reflection on sustainability:
- The thesis discusses how the project can affect sustainability directly and indirectly.
- The thesis discusses challenges that may arise from sustainable solutions, i.e., dilemmas where different considerations must be weighed against each other.
- The thesis not only mentions which sustainability goals and dimensions are relevant but also elaborates on why they are relevant to the specific project.
It can be wise to integrate sustainability assessments from the start of a project. This allows time to explore and evaluate potential sustainability impacts of the solution being developed or analyzed. In a development project, sustainability assessments can be very useful in identifying both functional and non-functional requirements for the solution.
In the final phase of your project, reflection on sustainability can help demonstrate the ability to critically reflect on possible consequences of the work/solution presented in the thesis.
Below you will find some hints on how to systematically and critically assess sustainability in your thesis.
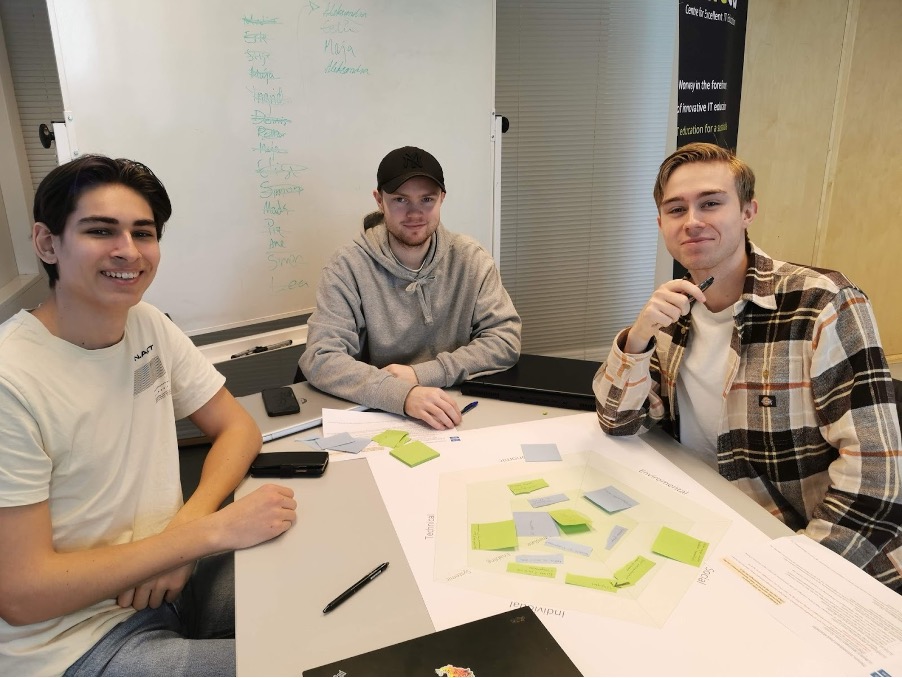


Photo: B.Krogstie/NTNU
Figure 1: Students working on sustainability analysis using SusAF
How to conduct a critical assessment/analysis of sustainability in your thesis
To integrate sustainability assessments in Bachelor’s and Master’s theses, it is advisable to start early in the semester. This allows sufficient time to explore and evaluate the different sustainability impacts of the solution being developed or analyzed, ideally in collaboration with the project supervisor. As a tool to structure a sustainability analysis, we have chosen to focus on the SusAF framework. There are other frameworks that also work well, but we have chosen to focus on this one. We recommend the following steps to effectively use SusAF:
- Familiarize yourself with the framework
- Become familiar with the five dimensions of sustainability in the framework: social, individual, environmental, economic, and technical sustainability.
- Understand the different levels of sustainability impacts: immediate, enabling, and structural.
- Identify sustainability impacts related to the solution in your thesis
- Use SusAF guiding questions to identify potential impacts within each dimension.
- Assess both positive and negative consequences.
- Identify potential connections between impacts, i.e., where one impact can lead to another.
- Document assumptions
- You will likely need to make some assumptions to predict sustainability impacts.
- Note which conditions and assumptions the analysis is based on.
- Present the analysis in table and/or figure format
- Discuss and evaluate the findings
For a more detailed guide on using the SusAF framework, refer to SusAF Taster, where you will find which questions to ask to identify sustainability impacts, and how to proceed.
Once sustainability impacts have been identified, they can be presented in a table and/or figure to get a good overview of how they influence each other. Here is a simplified example:
| ID | Impact | Level | Affects | +/- |
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 7 |
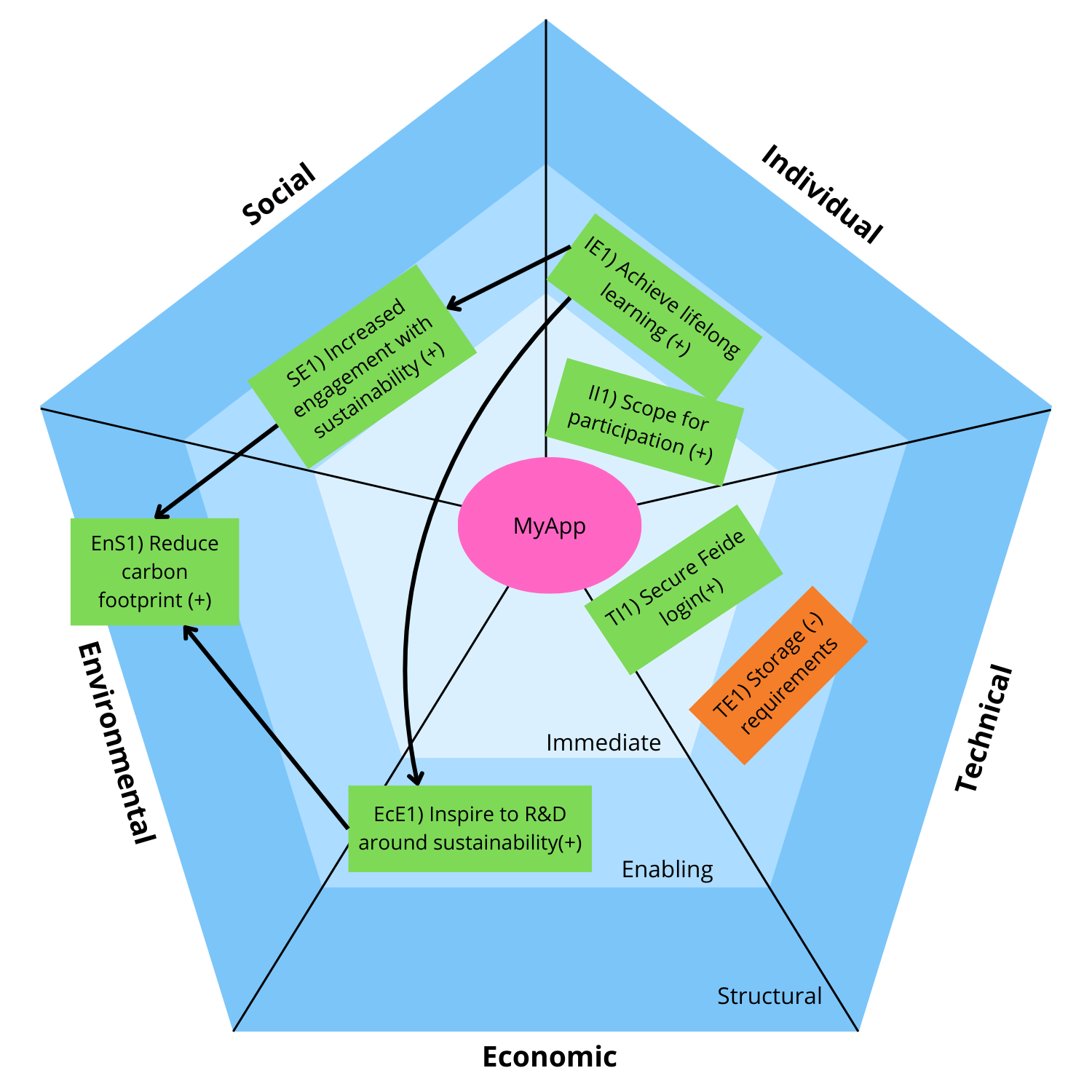


| ID | Impact | Level | Affects | +/- |
| II1 | Scope for participation | Immediate | + | |
| IE1 | Achieve lifelong learning | Enabling | SE1, EcE1 | + |
| SE1 | Increased engagement in sustainability | Enabling | EnS1 | + |
| EnS1 | Reduce carbon footprint | Structural | + | |
| EcE1 | Inspire research and entrepreneurship | Enabling | EnS1 | + |
| TI1 | Secure Feide login | Immediate | + | |
| TE1 | Requirements for storage space | Enabling | - |
Examples of sustainability analysis
Some examples of sustainability analysis for different types of assignments can be found here:
Click here for more examples of sustainability analysis for Bachelor/Master theses
Linking the thesis to the UN Sustainable Development Goals
When it comes to linking a Master’s or Bachelor’s thesis to the UN Sustainable Development Goals as stated in IDI’s course descriptions, a relevant question is whether the results of a sustainability analysis based on SusAF can be directly “translated” to the UN SDGs based on where the sustainability impacts are placed in the diagram.
The answer is: partially, but not completely. The so-called Wedding Cake model shows general relationships between the UN SDGs and various aspects of sustainability (economic, social, and environmental). This model can be useful for seeing connections at an overarching level.
In a critical reflection on sustainability in a specific case, it is necessary to go into more detail. For each sustainability impact you have identified in a sustainability analysis, you can assess which of the UN SDGs are relevant. It is recommended to consider not only the 17 overarching goals but also the more detailed targets, which make it clearer what the overarching goals encompass.
Don’t forget to consult your supervisor!
Your critical assessment of the thesis with regard to sustainability is something examiners will pay attention to. Therefore, it is advisable to consult your supervisor so that you receive useful feedback on your analysis and reflections on sustainability.
Give us feedback!
We would very much like to receive feedback from you that we can use for further development of this website! A simple feedback form that is quick to fill out can be found here.






