ZEB Definition
ZEB Definition
The ZEB definition and associated ambition levels were one of the core outcomes of the ZEB Research Centre, created to provide a clear and consistent framework for evaluating how far a building progresses toward true zero‑emission performance. These definitions describe different levels of life‑cycle emissions compensation, from operational energy to full material, construction, and end‑of‑life impacts, and are now widely used in research, design, and practice in various forms. Below, you can explore the five main ZEB definitions developed by the centre.
Zero Emission Building Definition
A zero-emission building produces enough renewable energy to compensate for the building's greenhouse gas emissions over its life span. The ZEB Research Centre has defined different levels of zero emission buildings depending on how many phases of a building's lifespan that are counted in. The 5 most important definitions, in rising ambition level, are:
ZEB – O ÷ EQ: The building's renewable energy production compensate for greenhouse gas emissions from operation of the building minus the energy use for equipment (plug loads).
ZEB – O: The building's renewable energy production compensates for greenhouse gas emissions from operation of the building.
ZEB – OM: The building's renewable energy production compensate for greenhouse gas emissions from operation and production of its building materials.
ZEB – COM: The building's renewable energy production compensate for greenhouse gas emissions from construction, operation and production of building materials.
ZEB – COMPLETE: The building's renewable energy production compensate for greenhouse gas emissions from the entire lifespan of the building. Building materials – construction – operation and demolition/recycling.
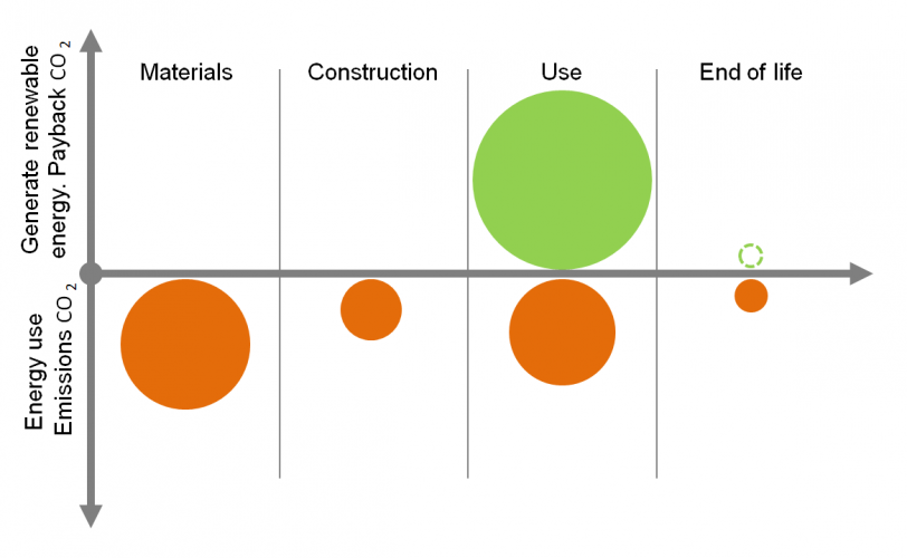
The illustration shows the different phases of a building's life that are included in the various ZEB definition levels. The renewable energy production (green circle) compensates for all greenhouse gas emissions throughout the life span of the building in the example.
