Vinylamide dimerization; “hidden acid” catalysis - Gold Catalysis in Organic Synthesis
Vinylamide cycloaddition dimerization; “hidden acid” catalysis
Through previous gold(I)-catalysed studies, we observed the "hidden acid" catalytic effect of a [AuSbF6 – alkyne] system. This protocol was further explored in order to develop a mild chemoselective head-to-tail vinylacylamide dimerization.
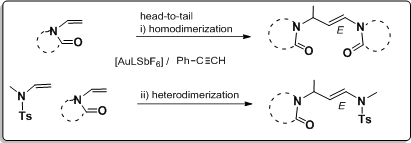
We studied the potential and limitations of head-to-tail cationic intramolecular homo-coupling of tertiary N-vinylacylamides and -sulfonamides, as well as the ability of such substrates to undergo more challenging hetero-dimerization.
The hidden acid catalysis by in situ generation of HSbF6 from the catalytic [Au[P(t-Bu)2(o-biphenyl)CH3CN]SbF6 – PhChCH] system allowed milder, more efficient and more convenient reaction conditions compared to other acid catalysis methods.
The results demonstrate the ability of
- vinylacylamides to effectively undergo homo- and hetero-dimerization to
- afford 1,3-N,N-functionalized (E)-but-1-ene products
- by the "hidden acid"[AuSbF6 – alkyne] protocol.
N. Iqbal; G. Blakstad; A. Fiksdahl Tetrahedron (2013) in print.
"Head-to-tail homo- and heterodimerization of vinylamides by hidden proton catalysis"