Model Augmented CT
Model Augmented CT
Model-augmented CT-based diagnostics of coronary artery disease. A next step from invasive to non-invasive assessment.
(Illustration: Model Augmented CT)
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of death in the world and represents a major burden for the healthcare system. The disease is caused by atherosclerosis which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries. In addition to lifestyle and dietary aspects, several local factors are related to the risk of future coronary events, including the degree of obstruction, the reduction in flow caused by the stenosis, the composition of the plaque, and shear stresses acting on the vessel wall.
Despite this fact, decision for revascularization is currently centered at regional hospitals with invasive coronary angiography (ICA) labs, and geometric evaluation remains the predominant factor used in decisions for revascularization in current clinical guidelines. Analyses of hemodynamics and plaque composition require additional expensive and invasive procedures and are only offered to selected high risk patients.
Framework
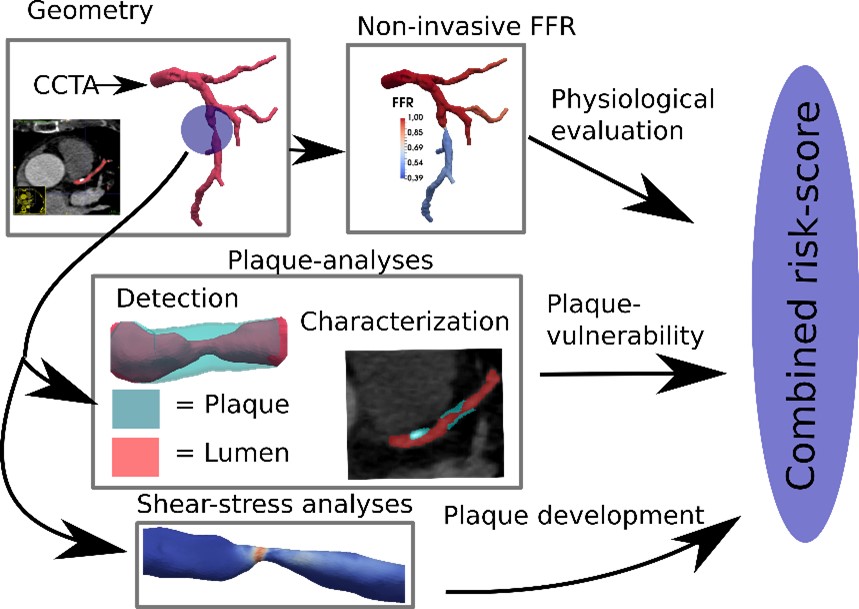
In this project we will build on our recently developed CT-FFR technology at NTNU and St. Olavs Hospital which enables hemodynamic evaluation of CAD based on Coronary Computed Tomography angiography (CCTA) images.
The framework will be developed further to include modules for plaque composition and shear stress analyses enabling a combined risk assessment from a single non-invasive CT-scan. Development will be performed on data from three already funded clinical trials from highly relevant CAD populations, where validation will be made by comparison with invasive data.
Funding
Model augmented CT is funded by Samarbeidsorganet.
Project leader
Project participants
-
Håvard Dalen Professor
+4772828027 havard.dalen@ntnu.no Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging -
Leif Rune Hellevik Professor of biomechanics
+47-73594535 +4798283895 leif.r.hellevik@ntnu.no Department of Structural Engineering -
Arve Jørgensen Associate Professor, Senior Consultant Thoracic Radiology
+4792283914 +4772828057 arve.jorgensen@ntnu.no Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging -
Synne Margrethe Sandberg PhD Candidate
synne.m.sandberg@ntnu.no Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging -
Rune Wiseth
+4772828145 rune.wiseth@ntnu.no Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging
Related projects:
Atheresclerosis
Model based diagnosis of coronary artery disease
Collaborators:
Prof. Lucian Mihai Itu, Transilvania University of Brasov
Associate professor Lucas Omar Muller, Emergency Clinical Hospital, Bucharest, Cardiology department
